Navigating the Dynamic World of Modern Web Development Using ReactJS
In the rapidly evolving digital landscape, the demand for dynamic, high-performing, and user-friendly web applications has never been greater. This imperative has spurred the proliferation of various JavaScript frameworks and libraries, each vying to empower developers in addressing complex programming challenges. However, the sheer volume and continuous emergence of these tools present a significant hurdle: identifying the most suitable framework that not only fulfills current project requirements but also ensures code quality, maintainability, and optimal execution.
“For web programmers, the framework selection process is critical, as it dictates the efficiency of development, the scalability of the application, and ultimately, the end-user experience.”
ReactJS, one of the most prominent JavaScript libraries, stands out as a powerful and efficient solution for building interactive, scalable, and modular web applications. Unlike comprehensive frameworks like Angular, React focuses solely on the "View" layer in the MVC architecture and empowers developers with unmatched control over UI rendering.
Core Concepts and Features of ReactJS
ReactJS distinguishes itself through a set of fundamental concepts and powerful features that collectively contribute to its efficiency, flexibility, and widespread adoption. These concepts enable developers to create complex UIs with ease while ensuring consistency and maintainability.
Component-Based Architecture
At the heart of ReactJS lies its component-based architecture. Rather than building monolithic pages, React encourages splitting the UI into small, reusable components. This modularity simplifies development, eases maintenance, and enhances collaboration across teams, especially in larger applications.
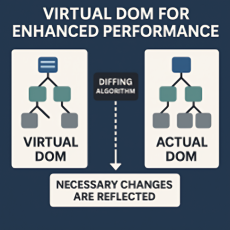
Virtual DOM for Enhanced Performance
React introduces a Virtual DOM—an in-memory representation of the real DOM. When state changes occur, React updates the Virtual DOM, compares it with its previous version using an efficient diffing algorithm, and updates only the affected parts of the actual DOM. This ensures fast, optimized rendering even in complex applications. This model avoids full-page re-renders, minimizing delays and improving the perceived responsiveness of the user interface. The decoupled and efficient nature of this process also enhances battery life on mobile devices and reduces CPU usage, making it ideal for performance-sensitive environments.
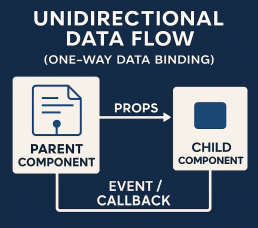
Unidirectional Data Flow (One-Way Data Binding)
React follows a unidirectional data flow where data flows from parent to child components via props. Child components communicate with parents using callbacks, making data flow predictable and manageable. This architectural approach greatly simplifies debugging and enhances performance. By maintaining this flow direction, developers can easily trace how data changes propagate through the application, enabling clearer state management. This is especially beneficial in large applications where maintaining control of state transitions is crucial to prevent bugs and ensure consistent user behavior.
JSX (JavaScript XML)
JSX is a syntax extension that allows developers to write HTML-like code within JavaScript. Although optional, it improves readability and development speed by enabling intuitive UI declarations. It brings the power of JavaScript into markup, allowing developers to write logic directly within the UI code.
Declarative UI
React allows developers to describe what the UI should look like for a given state. This declarative approach simplifies complex UI logic, resulting in more maintainable and predictable code. React then efficiently updates and renders the right components when your data changes.
Lifecycle Methods and Hooks
React class components provide lifecycle methods, while
functional components use Hooks such as useState and
useEffect to manage state and side effects effectively. These
features help structure component behavior over its life cycle.
How ReactJS Works
React builds a component tree representing the UI, compiles JSX into JavaScript using tools like Babel, and renders the result into the DOM. The entire process focuses on performance, maintainability, and modularity.
- Updates Virtual DOM
- Constructs a Virtual DOM tree reflecting the updated application state.
- Diffing Algorithm
- Compares new Virtual DOM with the previous one and detects minimal changes.
- DOM Updates
- Applies only the necessary updates to the actual DOM, ensuring fast performance and reducing unnecessary renders.
Why Developers Prefer React
React's simplicity, modularity, and performance have made it a favorite among developers worldwide. Whether working on a small project or a large enterprise-grade application, React provides scalable solutions with ease.
Performance
React's Virtual DOM and diffing algorithm contribute to high performance and blazing-fast rendering, making it a reliable choice for dynamic applications.
Strong Community Support
With extensive third-party libraries, components, and a large global community, React offers unparalleled developer support. Official Redux bindings and tools like React Router further enrich its ecosystem.
Cross-Platform Development
React Native enables mobile app development with the same knowledge base. The MERN stack (MongoDB, Express, React, NodeJS) offers full-stack JavaScript application development with a single language from frontend to backend.
Flexibility and Integrations
React allows integration with any backend or JS library. It is not opinionated and lets developers choose the best tools for their requirements, making it ideal for modular and scalable systems.
ReactJS vs Other Front-End Frameworks
ReactJS (Library)
Developed by Facebook, React focuses on the view layer, offering flexibility and excellent performance using the Virtual DOM. It's great for scalable SPAs and gives developers architectural freedom.
Angular (Full-Fledged Framework)
Angular, backed by Google, is a complete framework using TypeScript and built-in solutions. It has a steeper learning curve but offers comprehensive tools for large-scale applications with structured development practices.
Vue.js (Progressive Framework)
Vue combines the best of Angular and React with a low learning curve. It’s ideal for small to medium projects and offers official libraries for routing and state management.
Key Takeaways:
- Learning Curve: Vue is the easiest; Angular requires the most training.
- Performance: React leads with its Virtual DOM strategy.
- Community & Ecosystem: React has the widest third-party support.
- Scalability: Angular is most structured; React and Vue scale with add-ons.
- Flexibility: React allows maximum architectural freedom.
In conclusion, ReactJS remains a vital asset in a developer’s toolkit. Its performance, adaptability, and growing ecosystem make it an excellent choice for startups and enterprise projects alike. Whether you're building web or mobile apps, React provides the tools, speed, and community to build future-ready solutions.